THE WOOLY WORM RACE
FRACTIONS & METRIC UNITS
Represent, compare, order, and add fractions involving metric unit conversions.
Intentionality
Spark Curiosity
Fuel Sensemaking
During Moves
Student Approaches
Next Moves
Consolidation
Reflect and Consolidation Prompts
Resources & Downloads
Educator Discussion Area
Intentionality & Unit Overview
Length of Unit: 6 Days
Access each lesson from this unit using the navigation links below
To crown a champion for the Wooly Worm Race, students will represent and order the distances travelled by each caterpillar.
In this task, students will represent the distances travelled by each caterpillar using a concrete or visual model to order them from greatest to least. We have intentionally selected a linear context because we are hoping to emerge the bar model and eventually the number line as effective and efficient representations that can be used when working with fractions.
Some of the big ideas that may emerge through this task include:
- Fractions can be represented in a variety of ways;
- How you partition the whole determines the fractional unit (i.e.: partitioning a whole into 6 parts will result in 6 sixth parts);
- As you partition a whole into more parts, the smaller the size of each part;
- As you partition a whole into more parts, the larger the denominator;
- In order to compare two or more fractional quantities, the whole must be the same;
- The numerator indicates the number of parts relative to the number of parts in the whole indicated by the denominator; and,
- Fractional amounts exist between whole numbers.
Spark Curiosity
What Do You Notice? What Do You Wonder?
Show students the first minute of this video: Facilitator Note: In the actual “Wooly Worm Race”, the first caterpillar to the finish line wins. However, in this particular unit, we will be modifying the rules to better suit our learning goal. Be sure to stop the video after the first minute to avoid introducing information that will conflict with the context of this unit. Then, ask students:What do you notice? What do you wonder?Give students 60 seconds (or more) to do a rapid write on a piece of paper. Then, ask students to share with their neighbours for another 60 seconds. Finally, allow students to share with the entire group. Be sure to write down these noticings and wonderings on the blackboard/whiteboard, chart paper, or some other means to ensure students know that their voice is acknowledged and appreciated. Some of the noticing and wondering that may come up includes:
- I notice caterpillars.
- They are fuzzy.
- There are strings going up the wall.
- One of the caterpillar’s name is Silly Willy.
- I saw one named Scratchy.
- I think this is a competition.
- I saw someone who looked liked like a referee.
- There were at least 18 caterpillars.
Estimation: Prompt
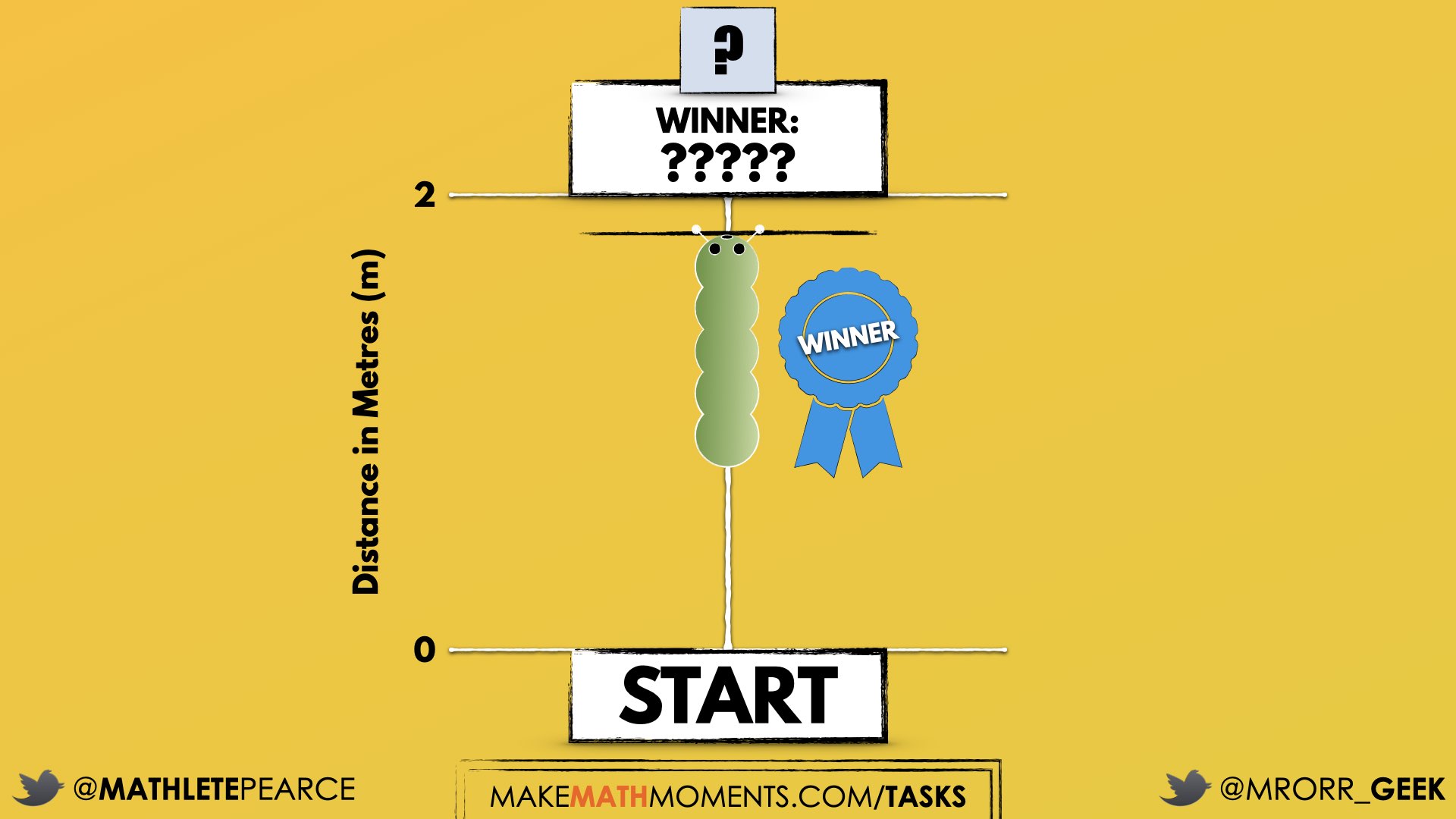
After we have heard students and demonstrated that we value their voice, we can land on the first question we will challenge them with:How far do you think the winning caterpillar climbed?We can now ask students to make an estimate (not a guess) as we want them to be as strategic as they can possibly be. This will force them to use spatial reasoning alone to try and come up with an initial estimate and to share it with their neighbours by trying to articulate why they believe their prediction is reasonable.
 Note in the image above that the distance is measured in metres and the winning caterpillar travelled less than the 2 m distance.
Consider asking students to think about a distance that would be “too low” and a distance that would be “too high” before asking for their best estimate in order to help them come up with a more reasonable estimate.
While any and all estimates should be acknowledged and welcomed, it might be helpful to encourage fractional language. For example, if a student gives a decimal quantity for an estimate stating something like “one point 8 metres”, encourage them to articulate what “point 8” means (i.e.: 8 tenths).
Let them chat with their neighbours and challenge them to an estimation duel or a math fight.
Note in the image above that the distance is measured in metres and the winning caterpillar travelled less than the 2 m distance.
Consider asking students to think about a distance that would be “too low” and a distance that would be “too high” before asking for their best estimate in order to help them come up with a more reasonable estimate.
While any and all estimates should be acknowledged and welcomed, it might be helpful to encourage fractional language. For example, if a student gives a decimal quantity for an estimate stating something like “one point 8 metres”, encourage them to articulate what “point 8” means (i.e.: 8 tenths).
Let them chat with their neighbours and challenge them to an estimation duel or a math fight.
While Students Are Estimating…
Monitor student thinking by circulating around the room and listening to the mathematical discourse. Encourage students to use precise mathematical language (including both standard and not standard units of measure) and positional language (in front, behind, on top…) to articulate their defense. If students’ estimates are unreasonable, encourage them to select a manipulative similar to what they believe the length of the string to be (perhaps linking cubes or a meter stick). While we hope to engage in learning around fractions including partitioning a whole to represent fractional amounts for the purpose of comparing, we will welcome students who share their estimates in decimal form and will not impose the use of fractions on them. Because the calculator is introduced to students so early in their mathematical journey, many students default to expressing fractional amounts as decimals without necessarily having a deep conceptual understanding of how they work. Later in this lesson and in this unit, we hope to continue building the conceptual underpinnings necessary for becoming flexible with fractions, decimals and even percentages. If students do estimate using decimals, be sure to help students by using appropriate language utilizing place value and the fractional language associated. For example, when a student intends to share 1.8, they may verbally describe this quantity as “one-point-eight metres”, we can use this opportunity to improve the conceptual understandings of all students by accepting that response, but reiterating as “one and eight-tenths of a metre”. Consider reiterating using more conceptually rich language such as:- 1.7 shared verbally as “one-point-eight” reiterated as “one and seven-tenths”
- 1.75 shared as “one-point-seven-five” or “one-point-seventy-five” reiterated as “one and seventy-five-hundredths”
- 1.85 shared as “one-point-eight-five” reiterated as “one and eighty-five-hundredths”
Fuel Sense-making
Crafting A Productive Struggle: Prompt
Since you have already taken some time to set the context for this problem and student curiosity is already sparked, we have them in a perfect spot to help push their thinking further and fuel sense making.
Share the total distance travelled by each of the caterpillars in the championship race:
Notice that the fractional amounts are expressed in words rather than standard-notation. We will work towards standard-notation throughout this unit, but for the time being, we want to emphasize the fractional unit. You will also notice that we are only working with a limited number of denominators, and they have been strategically selected.
Prompt students to:
Represent the distance travelled by each caterpillar and use your representations to order the distances from greatest to least.
During Moves
While Students Are Productively Struggling…
Monitor student thinking by circulating around the room and listening to the mathematical discourse. Select and sequence some of the student solution strategies and ask a student from the selected groups to share with the class from:
- most accessible to least accessible solution strategies and representations;
- most common/frequent to least common/frequent strategies and representations; or,
- choose another approach to selecting and sequencing student work.
The tools and representations you might see students using to convince their peers and/or the teacher include:
- Concrete manipulatives such a fraction strips or relational rods
- Paper folding
- A pictorial representation such as a bar model
- A number line
Have students share their strategies and reasoning for how to represent the total distance each Wooly Worm travelled and order them from greatest to least. Ask them to convince you and their peers that their answer is correct by sharing mathematical models.
Discuss their strategies and elicit student thinking during your consolidation to build off of their current prior knowledge and understanding rather than “fixing” or “funnelling” student thinking to a strategy and/or model that does not connect to their strategy and/or approach.
Student Approaches
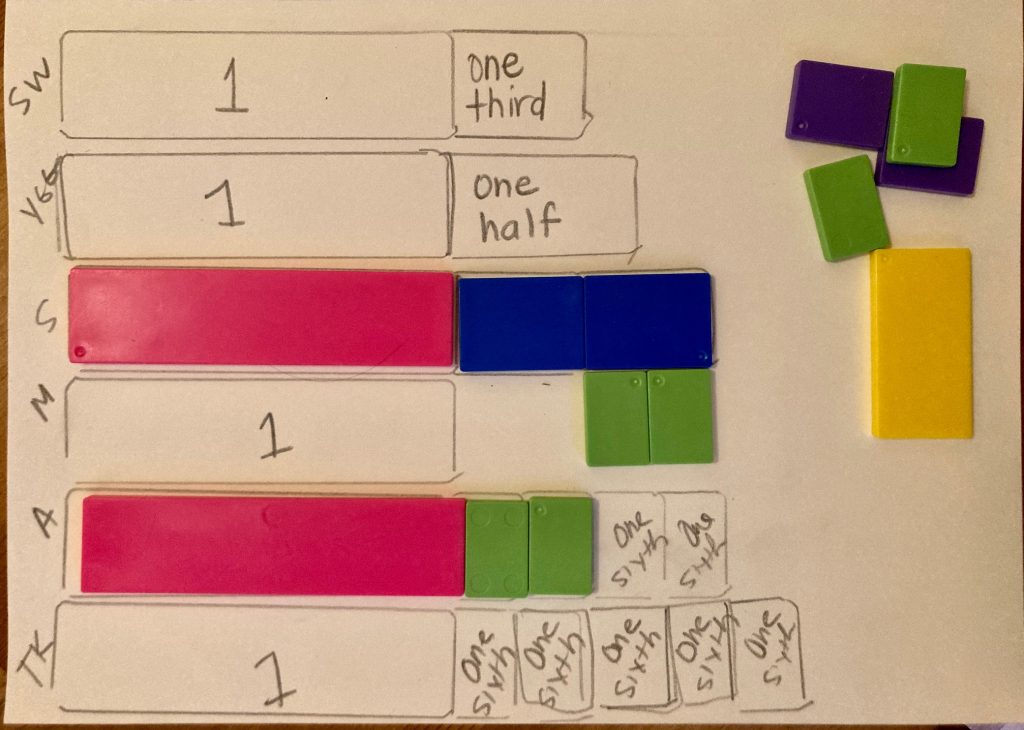
Student Approach #1: Fraction Strips
I used the fraction strips to represent the different caterpillars. I found the whole first, it was pink. And then I used the other pieces to find out which colour is a third and which is a sixth. I represented all of them except for Snowflake. Snowflake only travelled two-thirds of a metre, that is less than one, so I know that Snowflake came in last. Once I traced all of them, it was hard to tell who came in second, Scratchy or Abby. But I used the fraction strips, and I realized that two-thirds and four-sixths are the same, so they tied.
Student Approach #2: Paper Folding
I decided to use the strips of paper. I quickly realized that I didn’t have to worry about Molly and Snowflake. Snowflake was less than one metre, and Molly was one metre. So they finished in 6th and 7th. I decided to focus on the fractional amount that was more than one metre, because the remaining caterpillars all travelled one metre. With my paper strips, I saw that I would need to fold one strip into two parts, one into three and one into six parts, because all of the other caterpillars were half, thirds and sixths of a metre. Then I just marked where each caterpillar stopped at the fold in the paper.
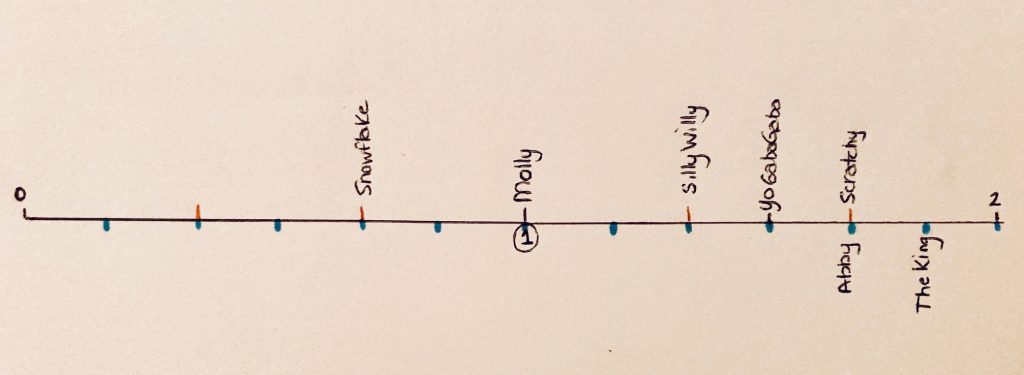
Student Approach #3: Number Line
I used a number line. I knew my number line would need to go from zero to two, because some of the caterpillars climbed less that one metre, and some climbed more. I started with Molly, and placed her at one. Yo Gabba Gabba was pretty easy also, halfway between one and two. Then I decided to mark all of the one-thirds, that let me place Silly Willy, Scratchy and Snowflake. I also needed sixths. I know that one sixth is
half of one third, so I split every third in half with a blue line. I decided to put the sixths on the bottom so that it was easier to see. I put Abby and the King in their spots. Then, it was easy to see the order.
This solution is only likely to emerge if students have prior experience using the number line as a tool.
Next Moves
Reveal
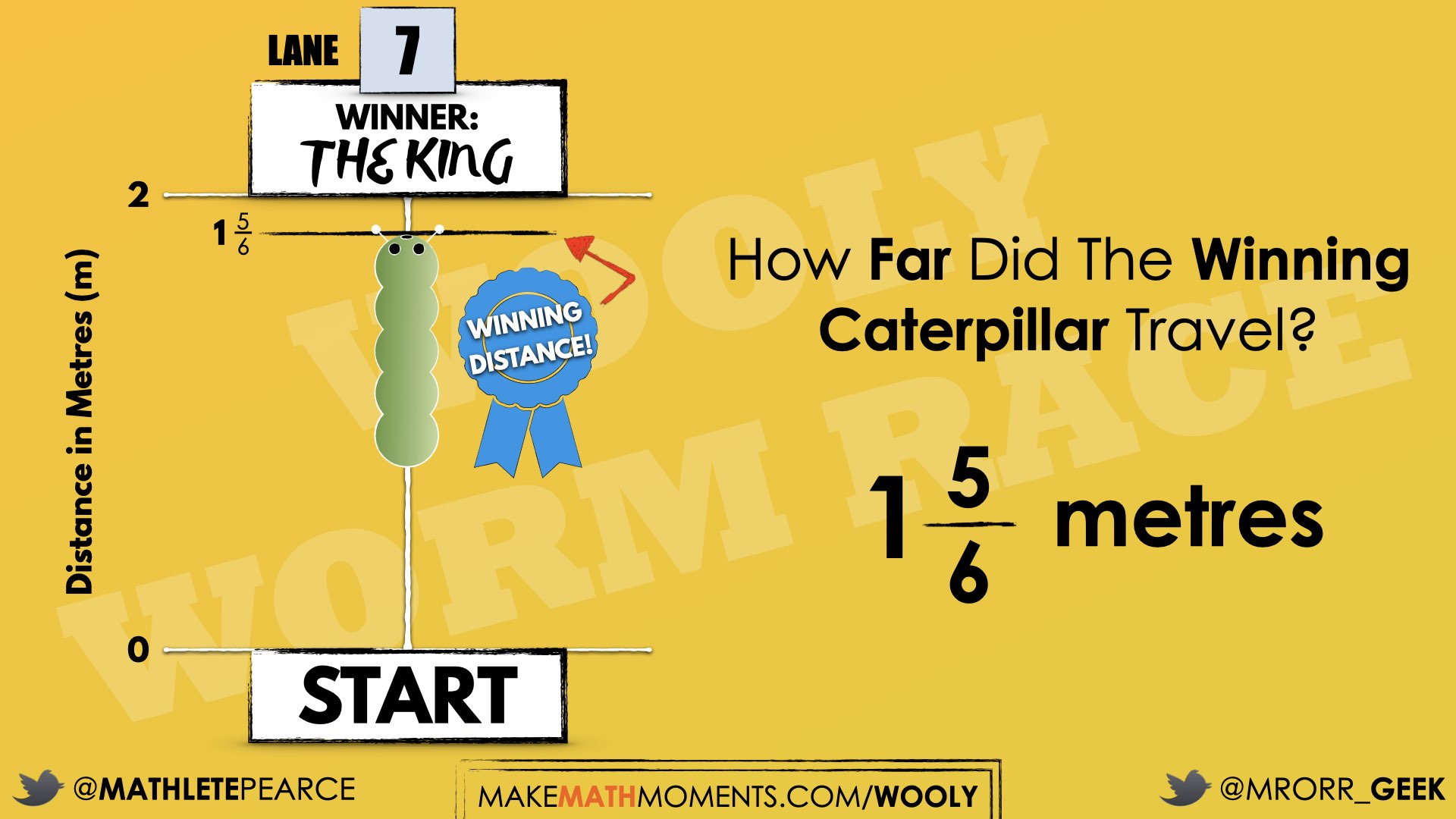
After consolidating learning by making connections using student generated solutions, you can share the following reveal video:
A still frame of the winning caterpillar is as follows:
Go back to student estimates from the Spark portion of the lesson to determine who had the closest estimate. Be sure to celebrate the student or students who were closest so that students realize that there was value in sharing with the group.
Did students use decimal notation and/or decimal language to share estimates at the beginning of the lesson? Consider extending from here in the Extend section to give students an opportunity to explore comparing and converting between fractions and decimals.
Consolidation
During today’s consolidation, the goal is to reveal the power of the concrete and pictorial linear model as a tool to represent, order, and compare fractions. Rather than leading students towards the idea of finding a common denominator (which could be beyond their level of conceptual understanding at this point), these models are an effective tool to reason through this scenario and demonstrate the skill of comparing and ordering fractions with unlike denominators. Through the consolidation, there is also a potential to emerge the idea of equivalence using different fractional units. For example, Scratchy and Abby reached the same point, but their distance was expressed using a different fractional unit.
You might consider expanding on this idea by asking students to express Yo Gaba Gaba’s distance using a different fractional unit as well to reveal that one-half is the same as three-sixths and one and one-half thirds.
The consolidation is your opportunity to address any misconceptions that may exist such as students who may have struggled to equi-partition their wholes, or to be mindful of the consistently congruent whole metre. Students may need more time to develop this spatial awareness in order to use the pictorial models effectively. Students may have believed that a fraction expressed with a different fractional unit cannot be equivalent. This lesson serves to reveal this big idea.
Facilitator Note: While there are many different connections that can be made through this consolidation, keep in mind that it is likely unreasonable to consolidate the distance of all seven caterpillars and keep your students engaged. Be intentional about which caterpillars you’d like to use during the consolidation in order to be clear and concise without losing the attention of your learners.
Here is a silent solution animation that unpacks some of the thinking that can be explored:
Extend
As mentioned earlier in the lesson, many students likely shared their estimate for the distance travelled by the winning caterpillar using decimal notation and/or informal decimal language such as “one-decimal-8”.
This provides a great opportunity for students to explore comparing fractions and decimals as well as to build some understanding of equivalence between the two representations of fractional quantities.
Prompt students by saying:
Whose estimate was closest to the actual distance?
How can you convince your mathematics community?
You might consider sharing this screenshot:
The intention of this extension is to emerge the big idea that quantities represented as a decimal are fractions limited to base ten denominators (i.e.: tenths, hundredths, thousandths, etc.) and that we can leverage an understanding of fractional equivalence to convert between fractions and decimals.
If students claim that a certain estimate such as 1.8 metres was the closest estimate, consider asking students to share how they would model that this is true.
By shading a whole metre and partitioning a second metre into tenths and shading in 8 tenths, students can now compare this model side-by-side with the model of The King’s distance of 1 and 5 sixth metres.
If students suggest that a more precise estimate was closer such as 1.85 metres, this is a great opportunity to ask students how we can represent this quantity. Highlighting how partitioning 1 tenth into tenths will yield 10 hundredth parts can be extremely helpful for conceptualizing the relationship between fractions and decimals.
Watch this short silent solution video to build your own understanding of how fractions and decimals are related so you can leverage this understanding during the consolidation of this extension:
A screenshot of the final frame is shown below:
It is worth noting that 1.83 metres is an approximation, since a deeper exploration of the representation of 1 and five-sixth metres would result in a repeating decimal value of 1.833333… which may be worth exploring more deeply with your group of learners.
Reflect and Consolidation Prompts
Provide students an opportunity to reflect on their learning by offering these consolidation prompts to be completed independently.
Consolidation Prompt:
In last year’s competition, Silly Willy travelled a distance of 1 and 6 tenths of a metre while Yo Gaba Gaba travelled a distance of 1 and 3 fifths of a metre.
Compare the results of these two caterpillars.
Who travelled the furthest and how can you convince your math community that you’re right?
We suggest collecting this reflection as an additional opportunity to engage in the formative assessment process to inform next steps for individual students as well as how the whole class will proceed.
Resources & Downloads
Printable Lesson Plan PDF
Videos, Images & Media Files
Apple Keynote Presentation
Powerpoint Presentation
Printable Consolidation Prompts
Educator Discussion Area
Login/Join to access the entire Teacher Guide, downloadable slide decks and printable handouts for this lesson and all problem based units.
Explore Our 60+ Problem Based Units
This Make Math Moments Lesson was designed to spark curiosity for a multi-day unit of study with built in purposeful practice, number talks and extensions to elicit and emerge strategies and mathematical models.
Dig into our other units of study and view by concept continuum, grade or topic!




![Wooly Worm Race [Day 1] - 10 - Extend Prompt - Whose estimate was closest](https://learn.makemathmoments.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Wooly-Worm-Race-Day-1-10-Extend-Prompt-Whose-estimate-was-closest.001-1024x576.jpeg)
![Wooly Worm Race [Day 1] - 12 - Extend Consolidate Reveal - Whose Estimate Was Closest Image](https://learn.makemathmoments.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Wooly-Worm-Race-Day-1-12-Extend-Consolidate-Reveal-Whose-Estimate-Was-Closest-Image.001-1024x576.jpeg)


